
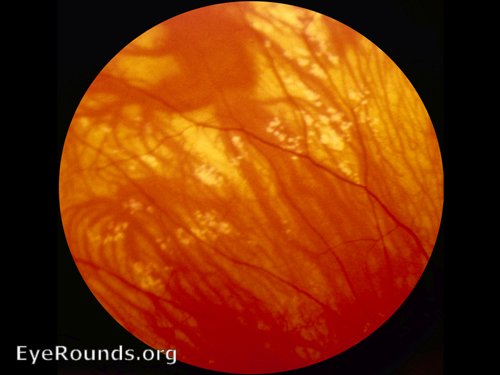
18 Genetic testing involves analysis of the APC gene and the MUTYH gene to distinguish between FAP and MUTYH-associated polyposis. 3, 4, 17 Classic FAP presents with hundreds to thousands of colonic polyps around the second decade of life, while attenuated FAP presents later in life with an average of thirty colonic polyps. 3, 6, 8, 15, 16 The degree of penetrance is unclear for the attenuated form but is nearly one hundred percent for the classic form. 3, 7, 8 The inheritance pattern of FAP is autosomal dominant and there is both a classic and attenuated form of this syndrome thought to be related to the location of the deletion in APC, though distinguishing the two forms is ultimately a clinical diagnosis. The mutated gene responsible for FAP is the tumor suppressor gene APC. 1, 5, 9, 14 If any of these are present on exam it is reasonable to refer for complete gastroenterological work up. The exam findings that distinguish FAP-associated CHRPE lesions are (1) bilateralism, (2) occurrence in multiple quadrants, (3) pisiform shape, and (4) irregular borders. However, they can be distinguished based on ocular exam. 5įAP-associated CHRPE lesions are histologically like classical CHRPE lesions. 10 Patients with classic CHRPE or Grouped Pigmentation of the Retina are not at a greater risk than the general population for developing colon cancer and the presence of these lesions does not warrant screening for FAP by colonoscopy or genetic testing. There has been no established relationship between classic CHRPE or Grouped Pigmentation of the Retina and FAP. It usually lacks halos, occupies one quadrant, and is comprised of smaller lesions than classic CHRPE and FAP-associated CHRPE. Grouped Pigmentation of the Retina is another CHRPE variant made up of multiple lesions, giving it the appearance of animal tracks and the nickname “bear tracks”. 11 However, blindness can develop as the lesion grows and gives way to exudative retinal detachment. 11, 12 Classic CHRPE lesions also exhibit diameter growth in the majority of cases, but malignant transformation to adenocarcinoma only occurs in one percent of cases and there have never been reports of metastasis. 1, 9, 11, 12, 13 The degeneration of photoreceptors is progressive and is linked to visual field defects. 5, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14 Pathological findings consist of retinal thinning, photoreceptor loss, and increased thickness of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). 1, 5, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 It is a flat lesion and can be pigmented or non-pigmented, although pigmented lesions are much more common. 13Ĭlassic CHRPE is unifocal and typically located in the mid-periphery of the fundus. 9, 12 This results in hypo-autofluorescence of the CHRPE lesions. 9, 10, 11, 12 The lack of lipofuscin is due to a dysfunction in phagocytosis and the catabolism of shed photoreceptor membranes. 1, 9, 10, 11, 12 They contain many large spherical melanosomes and have no lipofuscin granules. The retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells that constitute all types of CHRPE lesions are columnar to cuboidal and taller than the unaffected surrounding RPE. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 No differentiation has been made in nomenclature between the benign variants of CHRPE and the FAP-associated version despite risk of severe consequences associated with overtreatment or missed diagnosis.
#BEAR TRACKS RETINA SKIN#
Biopsies of the gastric polyps showed fundic gland polyps.įAP is an autosomal dominant syndrome that causes numerous colonic polyps that result in colorectal cancer by age thirty-five in ninety-five percent of cases and can be associated with multiple extracolonic features: desmoid tumors, epidermoid cysts, osteomas, numerous dental abnormalities, skin cancers, and CHRPE. EGD revealed multiple 2–3 mm sessile gastric polyps in the gastric fundus. At six months, a pouchoscopy was performed along with an EGD. Analysis of the MUTYH gene was normal.ĭue to the presence of polyps throughout the colon and rectum and the presence of symptoms, a complete proctocolectomy was performed and well tolerated. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene sequencing showed a deletion of 5 nucleotides, denoted as APC 3183del5, which results in premature truncation of the APC protein at amino acid 1062 located in the middle of the gene. Polyp biopsies revealed tubular adenoma that were negative for high-grade dysplasia or malignancy. The polyps were both sessile and pedunculated, and ranged from 1 to 3 cm in size. The colonoscopy revealed hundreds of polyps extending from the rectum to the distal colon. Although family history was negative for colon cancer, a referral for a diagnostic colonoscopy was made.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
